February 09, 2026
Best All-in-One Solar + Storage Solutions for Homeowners: How Saxony Home Achieved Energy Independence with SolaX (2026)
Share my #SolaXStory
All-in-one solar + storage is no longer a niche upgrade. For many homeowners, it is becoming the most practical way to turn a solar power system into a reliable, flexible energy solution that can cut bills, raise self-consumption, and keep lights on during grid trouble.
In this ultimate guide, you will learn how a modern solar energy system is built, how the inverter and inverter battery work together, and how smart energy software turns hardware into a controllable energy storage system. You will also see how a real residential solar system in Saxony (Sachsen), Germany used SolaX hybrid inverters plus a solar battery system to reach 29 kWh of storage capacity.
 Core Foundations
Core Foundations
System architecture: solar PV plus energy storage system
A typical residential solar energy system has three main power paths:
PV to home loads: your solar pv runs appliances directly when the sun is out.
PV to battery storage for home: surplus solar charges the solar battery.
Grid to home and grid to battery: the grid supplies gaps, and can also charge batteries if tariffs make that useful.
A hybrid inverter is the traffic controller. It decides when to convert DC from the photovoltaic system to AC for the home, when to charge the battery, and when to export to the grid. Without a hybrid solar inverter, you often need extra boxes and more wiring to achieve the same behavior.
Software stack: monitoring, automation, tariffs, and smart energy management
Hardware alone does not maximize savings. Software closes the loop by turning measurements into actions:
Monitoring: real-time and historical views of PV generation, loads, and battery state
Control: schedules for charging, discharging, and EV charging windows
Alerts: fault notifications and performance drops (such as shading or a string issue)
Optimization: rules that target self-consumption or time-of-use shifting
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that electricity prices rose 6.7% from December 2024 to December 2025, reinforcing why homeowners increasingly care about optimization rather than generation alone. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, utility gas prices also rose in the same period.
All-in-One ESS System Design
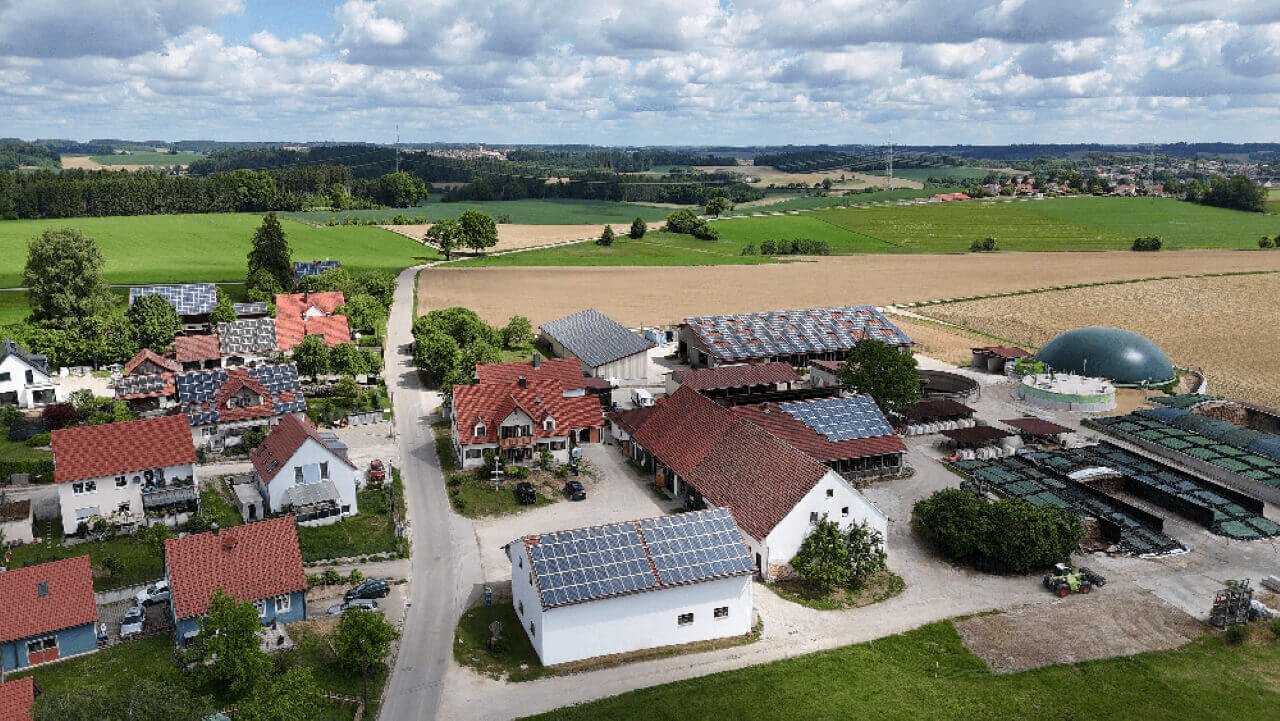
A real-world reference: Saxony home energy independence system
In Saxony (Sachsen), Germany, one homeowner project documented a system with:
PV module output: 3 kW
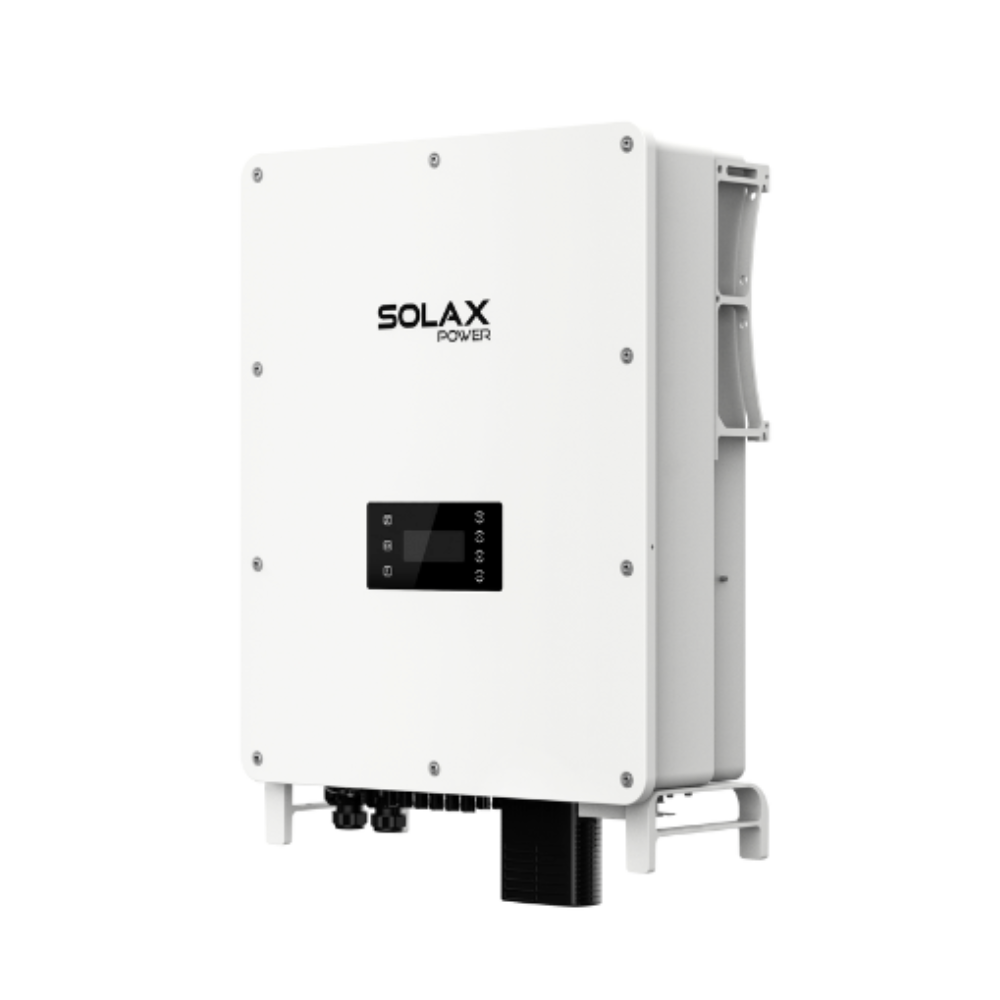
Hybrid inverter: 3 pcs of X3-HYB G4 Pro
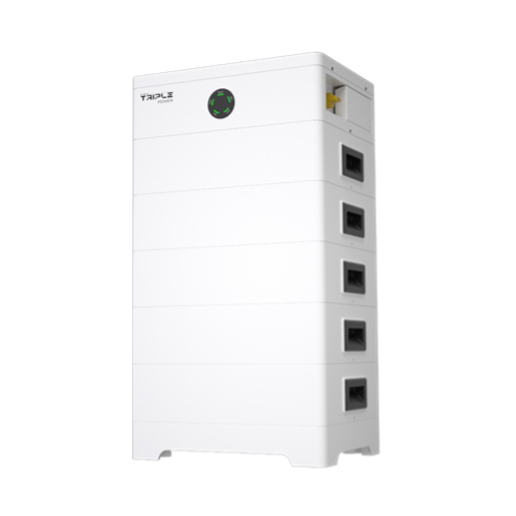
Battery system: paired with a T58 LiFePO4 battery system
Gross storage capacity: 29 kWh
This is a useful mental model because it highlights a common goal: high solar self-consumption with enough battery storage to smooth daily peaks and ride through short outages.

Step-by-step design workflow for homeowners
Use this workflow before you talk to a solar installer or finalize equipment:
List critical loads and comfort loads
Critical: fridge, lights, Wi-Fi, medical devices.
Comfort: HVAC, cooking, laundry, EV charging.
Measure your load profile
Look for morning and evening peaks.
Identify large surge loads (HVAC compressor starts, well pumps).
Choose a control goal
Self-consumption first (reduce exports).
Backup first (prioritize battery reserve).
Time-of-use shifting (charge and discharge on schedule).
Size PV for annual energy and roof constraints
Roof azimuth and shading can matter as much as nameplate size.
Size battery for the job, not the marketing number
Define backup hours for critical circuits.
Define peak-shaving target if you have demand charges.
How the hybrid inverter powerflow makes it work
A hybrid inverter enables three control moves that define the all-in-one experience:
Charge capture: when PV exceeds load, route energy into the solar battery instead of exporting.
Discharge shaping: when the home peak hits, discharge the inverter battery to reduce grid imports.
Backup transfer: isolate from grid and continue supplying selected loads during outages.
If you want near-seamless backup for sensitive electronics, pay attention to switchover behavior and how the system is wired (critical-load panel vs whole-home backup). Even the best inverters cannot overcome poor circuit planning.
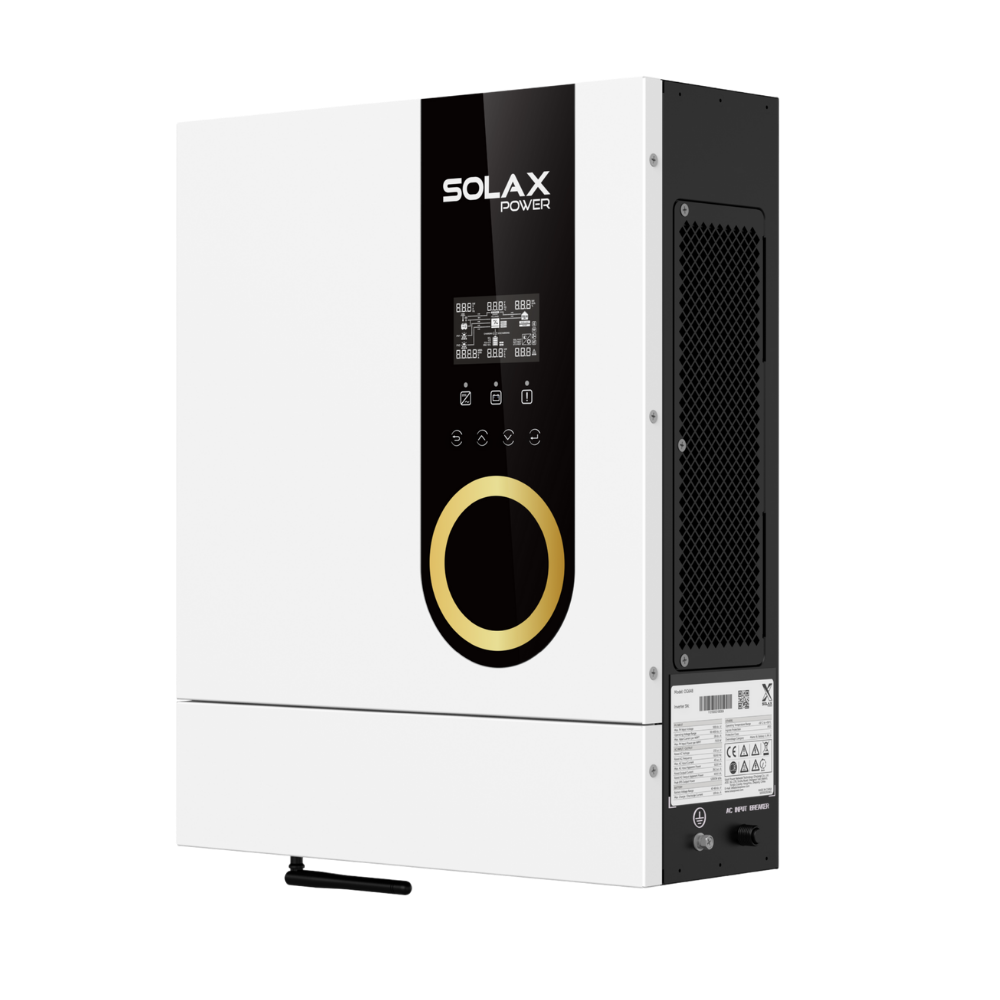
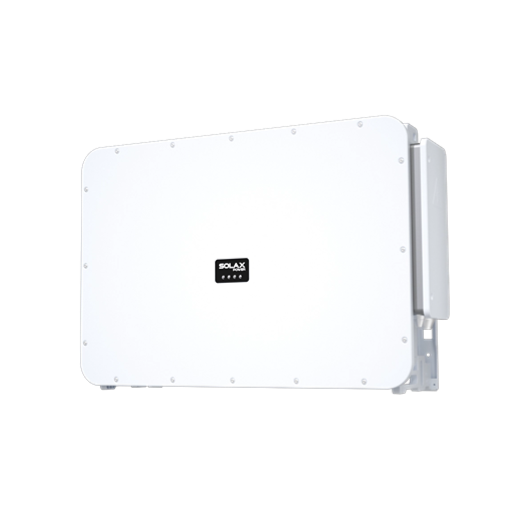
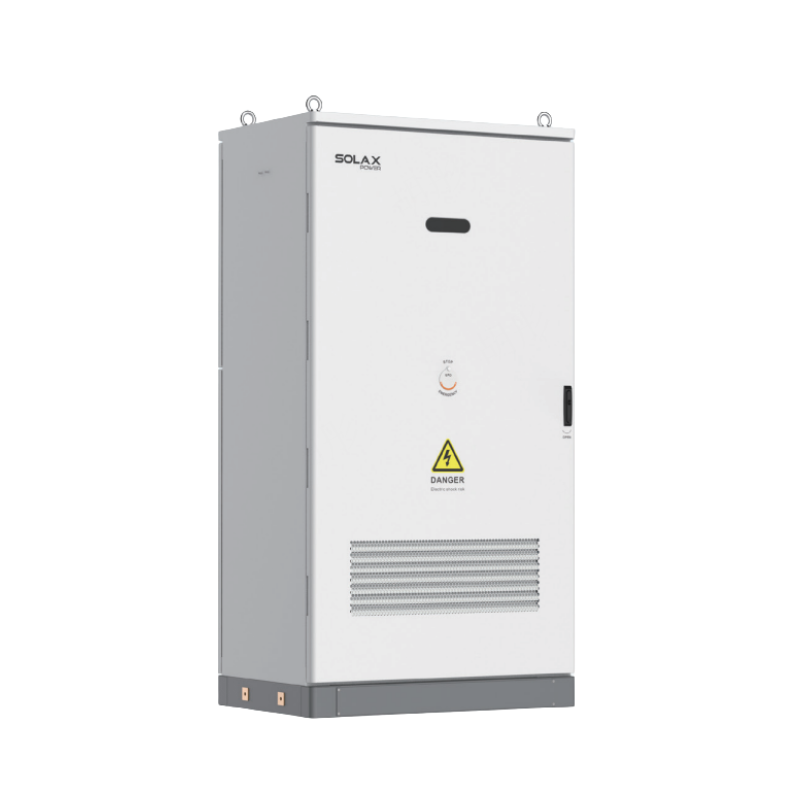
Product spotlight: integrated all-in-one ESS option
For homeowners who want fewer boxes and faster installs, an all-in-one energy storage system can reduce complexity. One example is the SolaX X-ESS G4, positioned as a plug-and-play all-in-one ESS with fast installation claims and support for smart energy management such as cloud monitoring.
It is described as supporting high PV oversizing, high efficiency, and operation across a wide ambient temperature range. That combination can matter when you are pushing a solar power storage plan hard in winter or during heat waves.
Product spotlight: X-ESS G4
Smart Energy Management and Monitoring
Why monitoring is part of the energy storage system, not an add-on
Homeowners often treat monitoring as a nice dashboard. In reality, monitoring is a control dependency.
Without accurate telemetry:
A hybrid inverter cannot reliably do zero-export control.
The battery solution may cycle at the wrong times.
You will miss early signs of PV underperformance.
As a practical rule, if you cannot answer these questions quickly, your monitoring setup is incomplete:
What percent of my daily solar energy is self-consumed?
When does my home import at the highest kW?
How many kWh did my solar battery charge and discharge yesterday?
Did my PV system clip because of inverter AC limits?
What smart energy automation looks like in a home
Good smart energy management is usually a small set of rules:
Battery reserve floor: keep 20-40% SOC for outage readiness.
TOU discharge window: discharge during peak rates.
Midday load shifting: schedule dishwasher, laundry, or water heating when PV is abundant.
Export shaping: cap export if your interconnection limits exports.
A Stanford-led analysis reported that many U.S. households could reduce electricity costs and better manage blackouts with solar plus storage, highlighting that the value is not only savings but also outage resilience.
According to the Stanford Report, around 60% of families could reduce electricity costs on average with solar-battery systems, while many could also meet a meaningful share of demand during outages.
EV Charging and Home Electrification
The EV charging problem in solar energy terms
An EV can become the largest flexible load in a residential solar system. That is good news if you manage it well.
Two common EV charging patterns cause higher bills even with solar pv:
Charging in the evening when PV is near zero
Charging at high power while the home is already at peak load
A solar EV charger strategy solves this by matching charging power and timing to your PV output, inverter limits, and panel capacity.
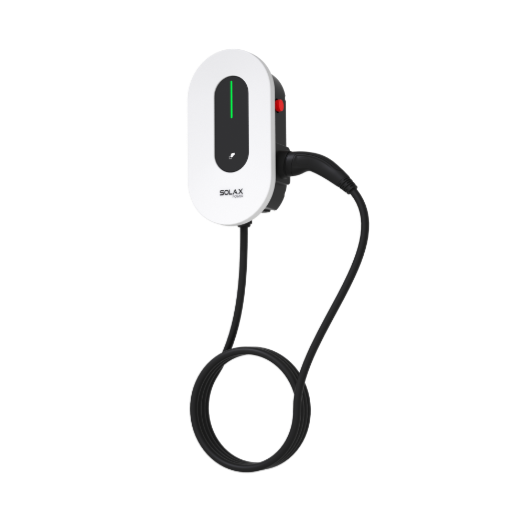
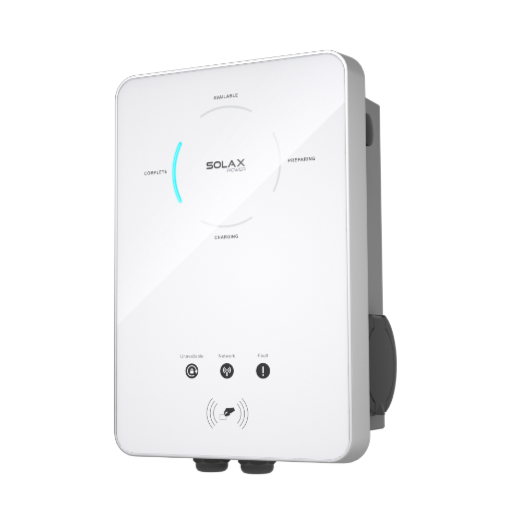
Product integration: Smart EV Charger G2 for controlled charging
A smart EV charger needs more than high kW output. It needs control, safety, and connectivity.
The SolaX Smart EV Charger G2 is listed with multiple power classes and emphasizes smart control and monitoring through cloud/app tools. Its published parameters include:
Models including X1-HAC-4, X1-HAC-7, X3-HAC-11, X3-HAC-22
Communication interface options: Wi-Fi, Ethernet, optional 4G, and RS485
Protection ratings listed as IP65 for plug type and IP54 for socket type
Physical dimensions shown as 206 x 390 x 139 mm
In practice, this matters because EV charging is a long-duration load. Reliable communications and load awareness reduce nuisance trips and help keep the rest of the solar power system stable.
Product integration: Smart EV Charger G2
Microinverter vs String Inverter Choices
The core difference: where MPPT happens
A string inverter runs MPPT at the string level. A micro inverter runs MPPT at the module level.
That difference drives real homeowner outcomes:
Shading tolerance: micro inverter solar setups can isolate the impact of a shaded module.
Roof complexity: multiple roof faces often favor microinverter layouts.
Troubleshooting: module-level data can speed diagnosis.
Expansion: adding panels later can be simpler with micro inverters.
Product integration: module-level control with X1-Micro 4 in 1 G2
If your site has partial shading or you want module-level control, microinverters can be a strong fit.
The SolaX X1-Micro 4 in 1 G2 is presented as a four-MPPT micro inverter family with multiple variants. Published parameters include:
Up to 97% max efficiency and 99.90% MPPT efficiency
Ingress protection rating IP67
Dimensions listed as 317 x 225 x 41 mm
Weight listed as 5.2 kg
MPPT voltage range listed as 22 to 60 V
For homeowners, the practical payoff is stable yield across uneven conditions, plus monitoring and control that can reveal exactly where production drops happen.
Product integration: X1-Micro 4 in 1 G2
Selection and Decision Guide
Inverter sizing decisions for a solar power system
Inverter sizing is not just matching PV nameplate to AC kW. It is matching the house behavior.
Consider:
Continuous loads: baseline usage that never turns off
Peak loads: cooking and HVAC coincidence peaks
Surge loads: compressor starts and pump starts
Future electrification: EV charging, heat pump installation, electric cooking
If you are using a hybrid inverter with backup, check whether the backup output (EPS) can handle the loads you expect during outages.
Compliance: interconnection and safety testing
Grid rules vary by region. Even in 2026, the practical homeowner lesson is the same:
Export limits, rapid shutdown rules, and permitted wiring methods can decide what is possible.
Use your installer to validate:
Inverter certifications for your jurisdiction
Battery installation requirements (clearances, fire code constraints)
Whether whole-home or partial-home backup is permitted
Decision framework table
Use this table as a quick way to map goals to design choices:
Home scenario | Key constraint | Recommended approach | Trade-off |
High bills under TOU | Peak import cost | Hybrid inverter + solar battery storage, scheduled discharge | More configuration effort |
Frequent outages | Backup reliability | Critical loads panel + fast transfer EPS path | May not back up HVAC |
Complex roof / shading | Uneven PV production | Microinverter design with module-level MPPT | More rooftop electronics |
Export capped or low export pay | Wasted solar energy | Battery + solar surplus EV charging | Needs solid monitoring |
Future utility incentives | Program uncertainty | VPP-ready platform with standard protocols | Requires connectivity |
Conclusion
Best all-in-one solar + storage solutions combine a well-sized solar pv array, a capable hybrid inverter, a durable solar battery, and smart energy management that actually matches your tariff and lifestyle.
The Saxony home example shows how a residential solar system can be built around hybrid inverters and a large battery bank to push self-consumption and resilience. Your best next step is to shortlist an energy storage system by scenario: bill reduction, backup, EV charging, or future VPP participation.
FAQ
Table of Contents
Last News
Explore expert insights, practical guides, and the latest news on SolaX Power.

To the Latest Newsletter
Stay Ahead with the Latest SolaX Updates!
Subscribe
I have read and agree to Privacy Policy and User Terms